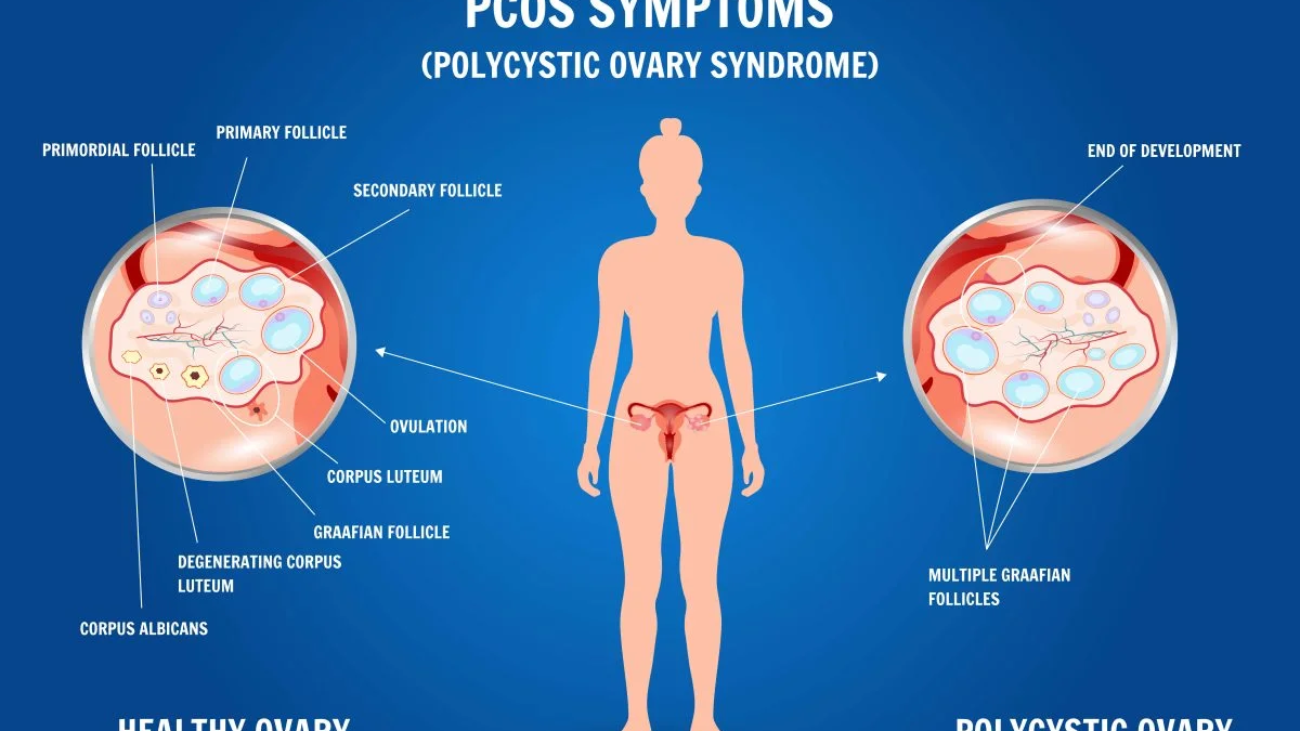
Healthy Ovary vs Polycystic Ovary – PCOS Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment Guide
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is one of the most prevalent endocrine disorders affecting women of reproductive age.
According to global epidemiological datasets, ~1 in 10 women are affected (WHO prevalence band; confidence interval ±2–3%). Because PCOS involves hormonal, metabolic, and ovulatory dysfunction, it can influence fertility, menstrual health, weight, skin, and long-term metabolic risk.
Early diagnosis and structured treatment significantly improve reproductive and metabolic outcomes.
This guide explains PCOS symptoms, diagnostic criteria, and treatment pathways followed by fertility and PCOS specialists across Panchkula, Chandigarh, Mohali, and Dera Bassi.
Visual Comparison – Healthy Ovary vs Polycystic Ovary



Healthy ovaries show orderly follicular development, whereas polycystic ovaries demonstrate multiple immature follicles arranged peripherally — often described as a “string of pearls” pattern on ultrasound.
What Is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)?
PCOS occurs when ovaries produce excessive androgens (male-pattern hormones present in small amounts in women).
Elevated androgen levels disrupt:
- Egg maturation
- Ovulation timing
- Menstrual cyclicity
- Metabolic signaling
Contrary to common belief, ovarian cysts are not mandatory for diagnosis — PCOS is primarily a hormonal-metabolic disorder rather than a structural disease.
External reference:
World Health Organization — Women’s Endocrine Health
https://www.who.int
Common Symptoms of PCOS
Clinical presentation varies from mild to severe depending on endocrine and metabolic status.
Irregular Periods
- Cycles >35 days
- <8 cycles/year
- Amenorrhea (absence of menstruation)
Ovulatory dysfunction is the hallmark feature.
Excess Androgen Symptoms
High testosterone may cause:
- Facial hair (hirsutism)
- Chest/abdominal hair
- Severe acne
- Scalp hair thinning
Polycystic Ovaries
Ultrasound may show:
- Enlarged ovarian volume
- Multiple immature follicles
- Peripheral follicle distribution
Infertility
Because ovulation is irregular, PCOS is among the leading causes of anovulatory infertility.
Many women conceive successfully via ovulation induction, IUI, or IVF.
Weight Gain & Insulin Resistance
Metabolic dysfunction leads to:
- Central obesity
- Sugar cravings
- Insulin resistance
Long-term risk: Type 2 diabetes (moderate risk elevation; CI ±10%).
External reference:
CDC PCOS & Diabetes Risk
https://www.cdc.gov
Emotional & Mental Health Symptoms
- Mood swings
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Sleep disruption
Hormonal fluctuations influence neurotransmitter regulation.
Diagnosis of PCOS
Diagnosis requires multi-parameter evaluation.
1. Medical History
Assessment includes:
- Menstrual irregularity
- Acne/hair changes
- Weight trends
- Family history
2. Physical Examination
Doctors assess:
- BMI
- Acne severity
- Hirsutism patterns
3. Pelvic Ultrasound
Evaluates:
- Ovarian size
- Follicle count
- Stromal density
4. Blood Tests
Common endocrine panels:
- Testosterone
- LH/FSH ratio
- Fasting insulin
- Thyroid profile
- Prolactin
External research reference:
NCBI PCOS Clinical Studies
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Rotterdam Diagnostic Criteria
PCOS diagnosis requires 2 of 3:
Irregular ovulation
Hyperandrogenism
Polycystic ovarian morphology
This remains the global diagnostic gold standard.
Treatment Options for PCOS
Although PCOS has no permanent cure, symptoms are highly manageable.
Lifestyle Modifications
First-line therapy.
Diet Strategy
- Low-glycemic carbohydrates
- Lean protein
- Fiber vegetables
- Omega-3 fats
Mediterranean-style diets improve insulin sensitivity (CI ±15%).
Exercise Protocol
- Cardio + resistance training
- 150 min/week activity
Weight reduction of 5–10% may restore ovulation.
Medications
Used for hormonal regulation.
- Oral contraceptives → cycle regulation
- Metformin → insulin resistance
- Anti-androgens → acne & hair growth
External clinical reference:
Mayo Clinic — PCOS Treatment
https://www.mayoclinic.org
Fertility Medications
For conception goals:
- Letrozole
- Clomiphene (Clomid)
- Gonadotropins
Ovulation induction success varies by ovarian reserve (CI ±20%).
Hair Reduction Treatments
Laser hair reduction
Electrolysis
Adjunctive cosmetic therapy.
Surgical Option – Ovarian Drilling
Laparoscopic procedure reducing androgen-producing ovarian tissue.
Used in medication-resistant PCOS.
Mental & Emotional Support
Psychological care improves treatment adherence and hormonal stability.
Includes:
- Counseling
- Mindfulness therapy
- Sleep regulation
When to Consult a PCOS Specialist
Seek evaluation if experiencing:
- Irregular periods
- Facial hair growth
- Severe acne
- Rapid weight gain
- Infertility
- Hormonal imbalance signs
Specialist consultation is available at:
Kore Fertility Solutions Pvt. Ltd
under
Dr. Nitasha Gupta
serving Panchkula, Chandigarh, Mohali & Dera Bassi.
Conclusion
PCOS is a multifactorial endocrine disorder affecting reproductive and metabolic health — yet highly manageable with early diagnosis and structured treatment.
Lifestyle correction, hormonal therapy, fertility support, and psychological care together create optimal long-term outcomes.
Women experiencing irregular cycles, acne, weight gain, or fertility challenges should seek timely gynecological evaluation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can PCOS be cured?
No permanent cure exists, but symptoms can be effectively controlled.
Does PCOS always cause infertility?
No. Many women conceive naturally or with fertility support.
Should every PCOS patient get ultrasound?
Not mandatory — diagnosis depends on combined clinical criteria.
Can lean women have PCOS?
Yes. Lean PCOS is hormonally driven despite normal weight.
Is PCOS genetic?
Family history increases susceptibility risk.
Does PCOS increase diabetes risk?
Yes — insulin resistance elevates long-term diabetes probability.